Instance Types
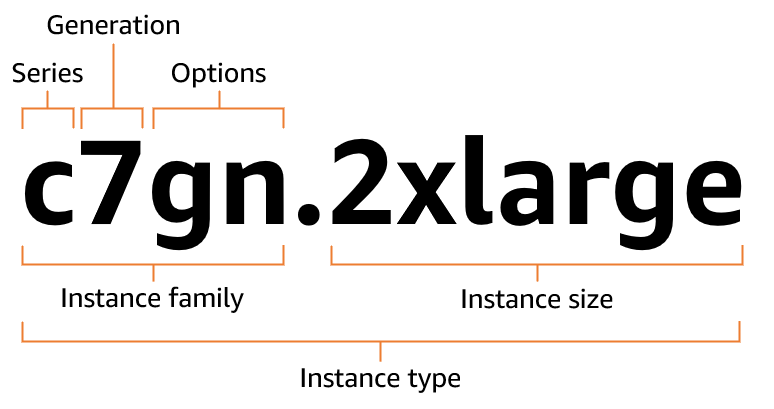
Naming Convention
Family.size → sizes scale from nano, micro, small ➡ up to 16xlarge or more.
Instance Comparison Tool
Instance Families
Each instance type belongs to a family optimized for a specific workload:
- CPU 🧮
- Memory 🧠
- Storage 💾
- Networking 🌐
| Family | Purpose | Series | 📌 Use cases | Latest Instances |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ⚖️ General Purpose | Balanced CPU, memory, and networking | M7, M8, Mac2 | Web servers, development, small databases. | M8g, M7i, M7i-flex, M7a, Mac2 (M2, M2 Pro) |
| 🧮 Compute Optimized | High-Performance CPU, lower memory | C7, C8 | High-performance computing (HPC), gaming servers, batch processing. | C8g, C7i, C7i-flex, C7a, C7gn, C7gd |
| 🧠 Memory Optimized | More RAM, less CPU. | R7, R8, U7 | In-memory DBs (Redis, Memcached), analytics, SAP. | R8g, R7i, R7a, R7iz, R7gd, U7i, U7in, U7inh |
| 💾 Storage Optimized | Fast, local storage (like NVMe SSDs). | I4, I7, I8 | NoSQL DBs, data warehousing, search engines. | I8g, I7ie, I4g |
| 🌐 Accelerated Computing | GPU/AI/ML or FPGA-based acceleration | G6, P5, F2, Trn2 | AI/ML, HPC, video rendering. | G6e, P5en, P5e, F2, Trn2, DL2q, Inf2 |
| 🚀 HPC (High Perf Comp.) | Scientific & tightly-coupled workloads | HPC7 | CFD, seismic analysis, weather modeling, fluid dynamics, large-scale simulations | Hpc7a, Hpc7g |