AWS ECS (Elastic Container Service)
A fully managed container orchestration service for running and scaling Docker containers on AWS. It eliminates the need to manage infrastructure while providing flexibility with different launch types.
ECS Launch Types
ECS provides two launch types for running containers:
EC2 Mode 🖥️
- Runs tasks on self-managed EC2 instances.
- You control instance types, networking, auto-scaling, and OS updates.
- Best suited when you want more customization and control over the infrastructure.
Fargate Mode ☁️ (Serverless)
- No need to manage EC2 instances, OS updates, or security patches.
- AWS automatically provisions compute resources.
- Best for serverless deployments and when you want less operational overhead.
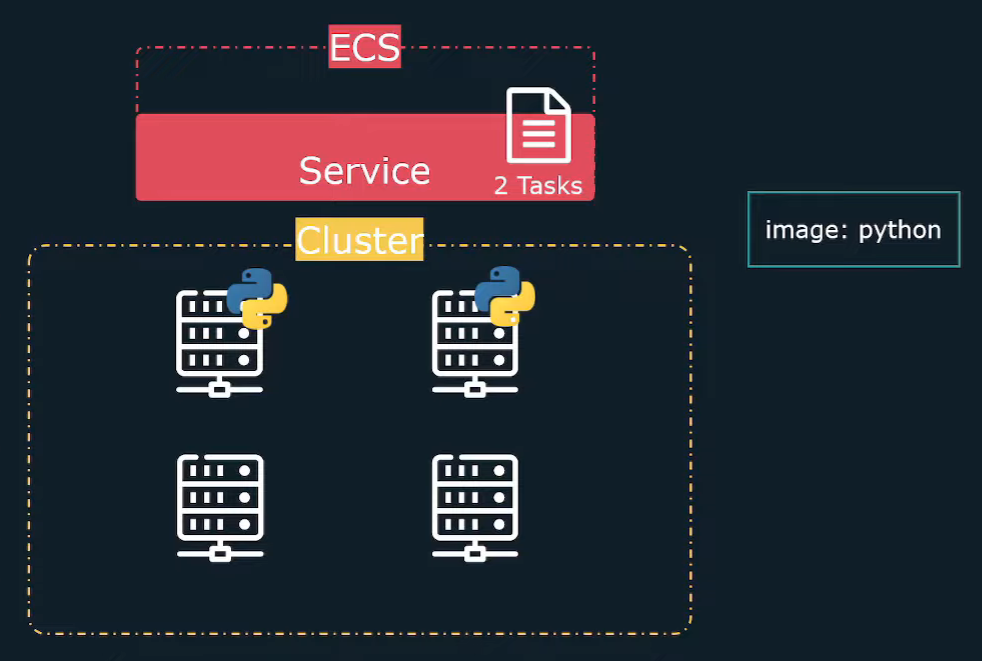
ECS Cluster
- A logical grouping of EC2 instances (in EC2 mode) or Fargate resources.
- Treats a pool of compute resources as an abstract unit.
- You don’t need to manage individual EC2 instances (IP addresses, hardware specs, etc.).
- Acts as a resource pool for running tasks and services.
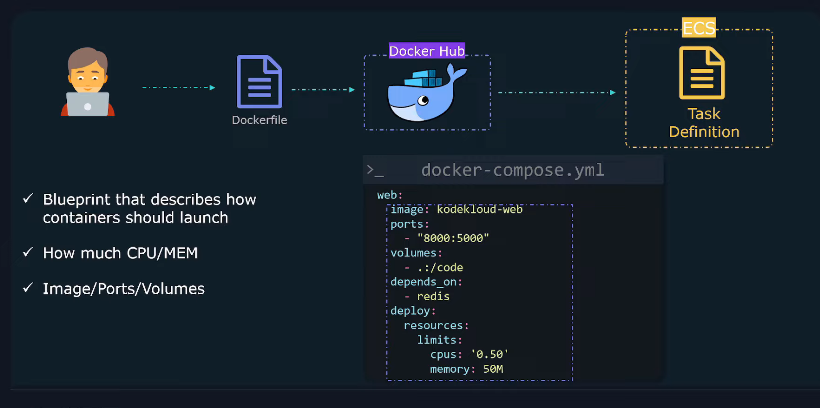
Task Definition (Container Blueprint)
A JSON-based template that defines how containers should run in ECS.
It includes:
- Container Image 📦 (from ECR/Docker Hub)
- CPU & Memory ⚙️ (resource limits)
- Port Mapping 🔌 (exposing container ports)
- Environment Variables 🌍 (configurable runtime settings)
- Volumes 🗂️ (persistent storage for containers)
Tip
Think of it as the Docker Compose equivalent for ECS.
Tasks (Running Containers)
- A task is a running instance of a Task Definition.
- Tasks run inside a cluster on EC2 instances or Fargate.
- Multiple tasks can run from the same task definition.
Task Scheduling ⏳
- Manual: Run tasks when needed.
- Service: ECS maintains the task count automatically.
- Event-Driven: Run tasks in response to CloudWatch events (e.g., scheduled jobs).
Info
Think of a task as a containerized microservice instance.
Services (Ensuring Availability & Scaling)
- Ensures that a specified number of tasks are always running.
- Self-healing:
- If a container crashes, ECS automatically restarts the task.
- If an EC2 instance fails, the task is rescheduled on another healthy instance.
- Auto-Scaling:
- Can increase or decrease the number of running tasks based on demand.
- Works with CloudWatch metrics (CPU, memory, request rate, etc.).
Tip
Services make ECS ideal for long-running applications (e.g., web apps, APIs).
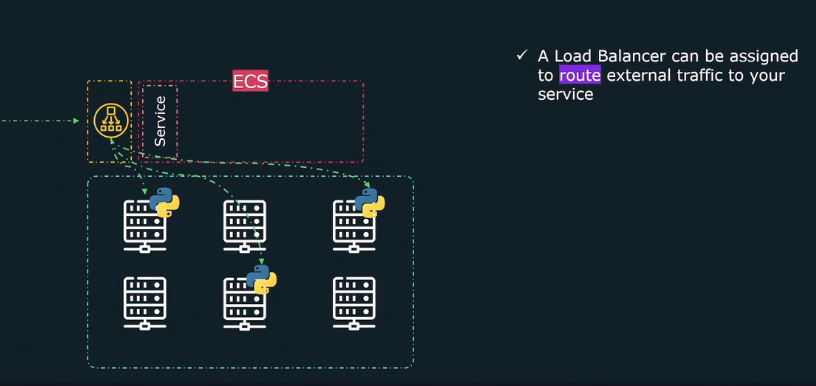
Load Balancers (Traffic Distribution)
- Distributes traffic across multiple running tasks.
- ECS supports:
- Application Load Balancer (ALB) 🌍 → Routes HTTP(S) requests based on rules (e.g., URLs, headers).
- Network Load Balancer (NLB) ⚡ → Routes TCP/UDP traffic with ultra-low latency.
- Automatically updates target groups when tasks scale up or down.
- Ensures high availability and even traffic distribution.
Tip
Load balancers make ECS services highly available and scalable.
ECS Security & Networking
- IAM Roles & Policies 🔑 → Control access to AWS resources (S3, DynamoDB, etc.).
- Security Groups & NACLs 🛡️ → Restrict inbound/outbound traffic.
- VPC & Subnets 🌐 → Define networking rules for ECS tasks.
- ECS Task Role 🎭 → Grants permissions to running containers for accessing AWS services.
ECS vs. Kubernetes (EKS) - When to Choose What?
| Feature | ECS 🚢 | EKS 🎡 (Kubernetes) |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Easier to set up ✅ | More complex setup ❌ |
| Management | Fully managed AWS service ✅ | You manage Kubernetes cluster ❌ |
| Flexibility | AWS-native, limited to AWS | Works across clouds ✅ |
| Scaling | Simple Auto-Scaling ✅ | Advanced Auto-Scaling ✅ |
| Networking | AWS-native integrations ✅ | More complex networking setup ❌ |
Info
Choose ECS if you want simplicity and AWS-native integration. Use EKS if you need multi-cloud flexibility or Kubernetes-specific features.
Steps to Create Your First Cluster
Create A Cluster
- Name/Launch type
- VPC/Subnet
- Cluster created
Create a Task Definition
- Launch type
- Task Def Name: taskDef1
- Task Role (ecsTaskExecutionRole)
- Make API call to aws service
- Pull container image from ECR
- push log to cloudwatch
- Operating system
- Task memory/CPU
- Add Container
- Container name - node-app
- Image Url
- Port mapping
- Task Def created
Create a Service
- Launch type
- Operating system family
- select Task definition: taskDef1 (Revision 1 latest)
- service name
- No of tasks ( desired tasks 2 )
- select same VPC/Subnets
- select security group ( what traffic allowed to service )
- set Auto Scaling of the tasks
- service created
Warning
Problem: both 2 tasks have 2 different public IPs. Always when one task crashes then new created to keep desired count, public IP changes.
Load Balancer
- one public ip common which will balance load across all tasks
Steps to Delete Your First Cluster
- Make desired task 0 by updating service
- Delete service
- Delete cluster