🌐 **Private IP, Public IP & NAT Gateway **
-
The college has many private IPs inside the campus LAN:
10.x.x.x 172.16.x.x 192.168.x.xThese are private IP ranges (not accessible from the Internet).
-
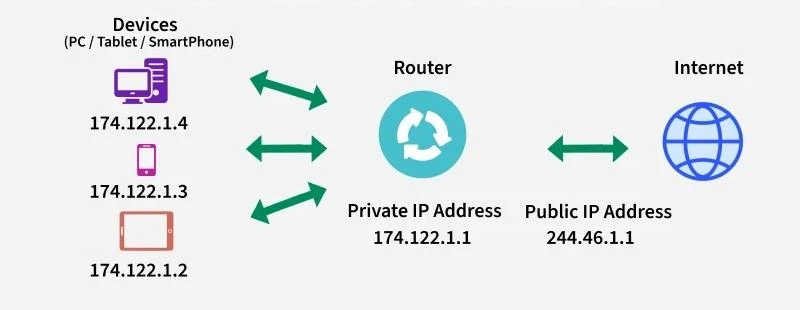
All devices — students’ laptops, lab PCs, Wi-Fi users — connect to the Internet through a central router or firewall.
-
That router performs NAT (Network Address Translation).
It replaces each private IP (like192.168.1.10) with the college’s single public IP when traffic goes to the Internet.
1️⃣ Public IP
✔ Definition:
A Public IP is an address that’s accessible over the Internet.
It’s assigned to resources that need to communicate outside the private network (e.g., web servers).
✔ Key Points:
-
Unique across the entire internet 🌍
-
Provided by ISP or cloud provider (like AWS)
-
Can be static (Elastic IP) or dynamic
-
Used for direct external communication
🧠 Example:
52.14.22.101 → Public IP of an EC2 instance accessible from your browser.
2️⃣ Private IP
✔ Definition:
A Private IP is used for internal communication within a private network (VPC, LAN).
It cannot be accessed directly from the Internet.
✔ Key Points:
-
Defined by RFC 1918 ranges:
-
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 -
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 -
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
-
-
Used for communication between internal servers (e.g., app → database)
-
Cheaper and more secure than using public IPs
🧠 Example:
10.0.2.15 → Private IP used inside a VPC subnet.
3️⃣ NAT Gateway (Network Address Translation)
✔ Definition:
A NAT Gateway allows instances in private subnets to access the Internet (for updates, APIs, etc.)
➡️ while preventing inbound traffic from the Internet.
✔ How It Works:
-
Private instance → sends request to Internet
-
NAT Gateway → replaces private IP with its public IP
-
Response → comes back to NAT Gateway → forwarded to private instance
✔ Key Points:
-
Deployed in a public subnet
-
Assigned a public Elastic IP
-
One-way communication: Outbound only
-
Used for security + outbound internet access
🧠 Example Use Case:
Private EC2 → needs to yum update → request goes via NAT Gateway → to Internet.
💡 Quick Comparison
| Feature | Public IP | Private IP |
|---|---|---|
| Internet Access | ✅ Direct | ❌ No |
| Used In | Public Subnet | Private Subnet |
| Security | Less Secure | More Secure |
| Visibility | Global | Local |
Would you like me to extend this with a small AWS architecture diagram (ASCII or image) showing how NAT Gateway connects private and public subnets?
| Feature | Public IP Address 🌍 | Private IP Address 🔒 |
| Definition | Assigned by ISPs and routable on the internet | Used within private networks (not routable on the internet) |
| IP Range | Comes from IANA-assigned public IP pools | Uses RFC 1918 ranges standard: 🔹 10.0.0.0/8 🔹 172.16.0.0/12 🔹 192.168.0.0/16 |
| Uniqueness | Globally unique (no two devices can have the same public IP) | Can be reused across multiple private networks |
| Internet Access | Directly accessible from the internet | Requires NAT (Network Address Translation) to access the internet |
| Example Usage | Websites, cloud servers, gaming servers | Home WiFi, corporate LAN, AWS VPCs, internal databases A home WiFi router assigns 192.168.1.10 to your laptop (private IP). |
| Security | Less secure (exposed to cyber threats) | More secure (not directly reachable from the internet) |
| Cost | Assigned & controlled by ISPs/cloud providers (can be paid) | Free to use within private networks |
| AWS Example | Elastic IP (EIP), EC2 Public IP | AWS VPC subnets, EC2 private IPs |