EBS and EFS Storage
AWS EBS (Elastic Block Store)
EBS Basics
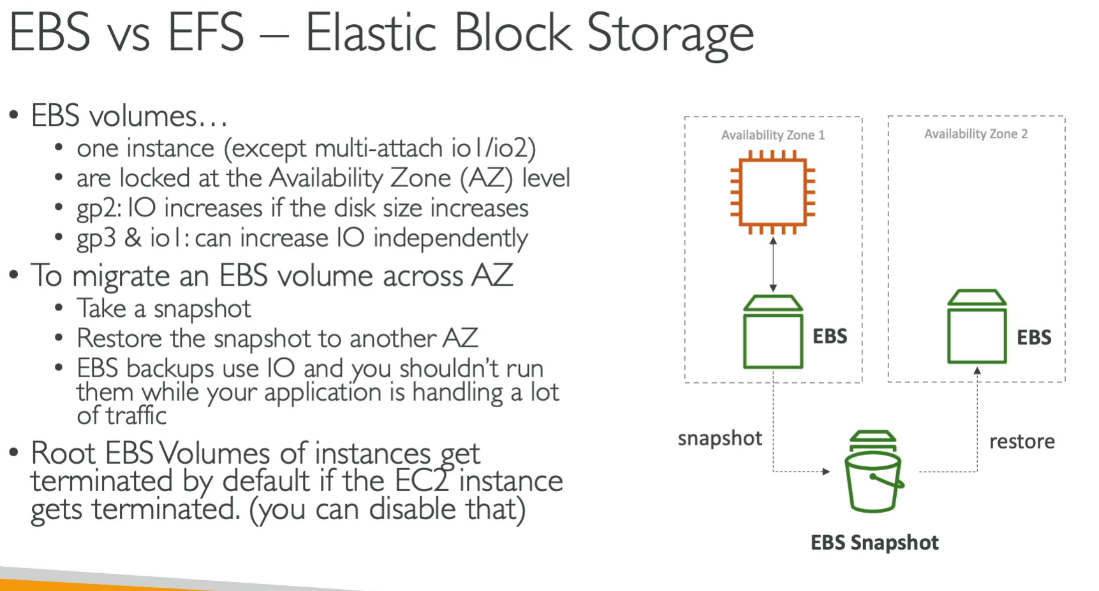
- Block-level storage service used with AWS EC2 instances
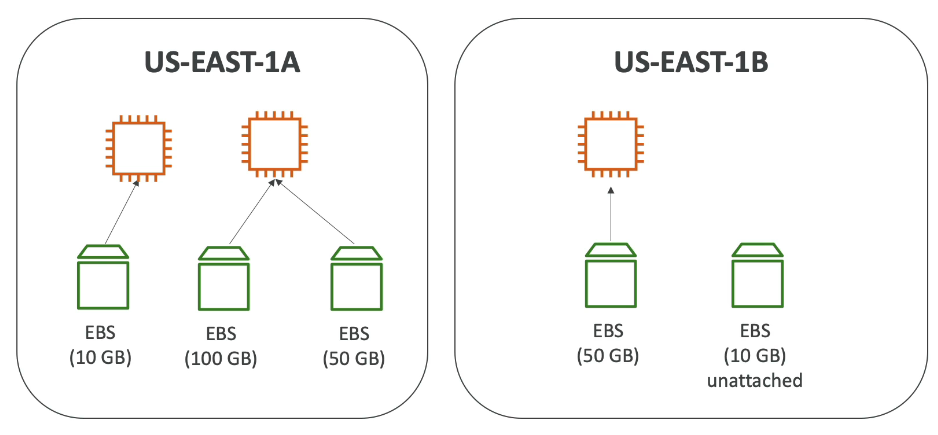
- EBS volumes are bound to a specific Availability Zone (AZ)
- Just like EC2, you can’t attach across AZs
Warning
📌 Root volume (/dev/xvda) is deleted on instance termination by default Other attached EBS volumes are not deleted unless specified
Snapshots
- EBS Snapshots are point-in-time backups of EBS volumes
Recycle Bin
- Protects EBS Snapshots and AMIs from accidental deletion
- You can set retention policies
Encryption
- You can encrypt an EBS volume using AWS-managed KMS key (aws/ebs)
Tip
💡 Use copy snapshot to: Create an encrypted snapshot from an unencrypted one
EBS Volume Types for Root Device
📌 Allowed types for boot volume:
- gp2 / gp3 – General Purpose SSD
- io1 / io2 – Provisioned IOPS SSD
Using lsblk to View Block Devices
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-180 ~]$ lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
xvda 202:0 0 8G 0 disk
└─xvda1 202:1 0 8G 0 part /
xvdb 202:16 0 5G 0 disk
xvdf 202:80 0 100G 0 disk- xvda: Root disk
- Mounted at /
- xvdb and xvdf: Additional attached volumes
- Not mounted by default - but you can mount it
Mounting xvdf (Quick Steps)
# 1. Check if it has a filesystem
sudo file -s /dev/xvdf
# 2. Format as ext4 (⚠️ Only if needed!)
sudo mkfs -t ext4 /dev/xvdf
# 3. Create a mount point
sudo mkdir /mnt/xvdf
# 4. Mount the volume
sudo mount /dev/xvdf /mnt/xvdf
# 5. (Optional) Add to /etc/fstab To auto-mount it after every reboot,
echo "/dev/xvdf /mnt/xvdf ext4 defaults,nofail 0 2" | sudo tee -a /etc/fstabEBS Volume Types Comparison
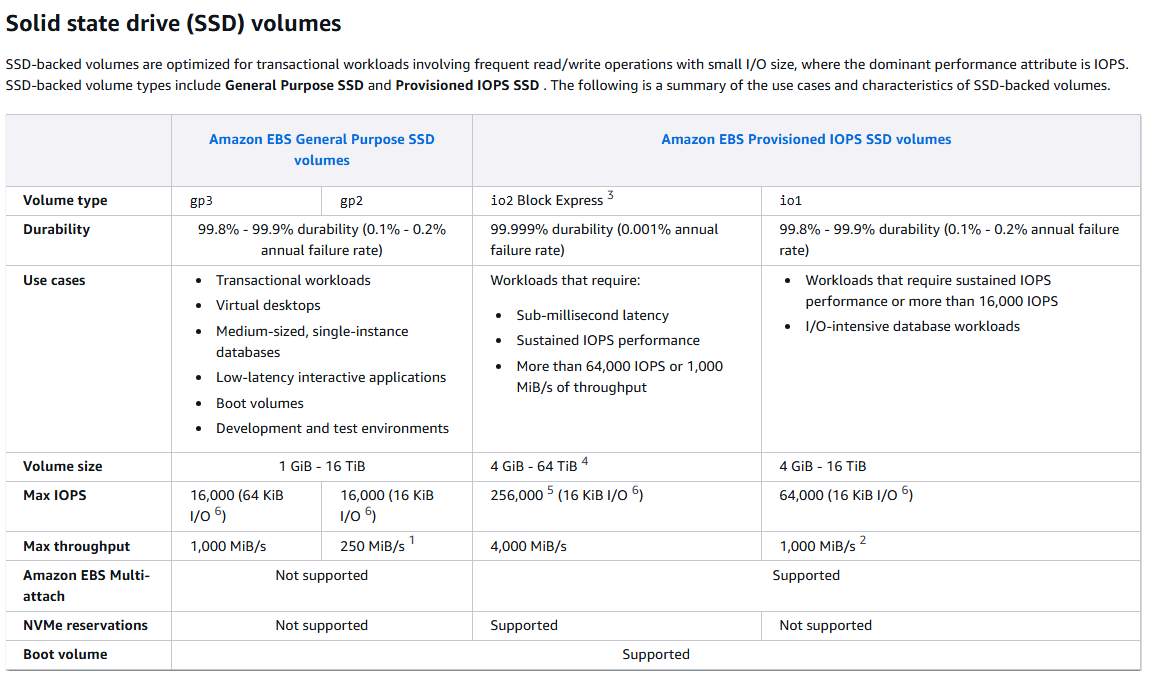
| Volume Type | Cost | Volume Size Range | Max IOPS | Max Throughput | Durability | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Purpose SSD (gp3) | $ | 1 GiB – 16 TiB | 16,000 | 1,000 MiB/s | 99.8%–99.9% | Boot volumes, small to medium databases, development and test environments |
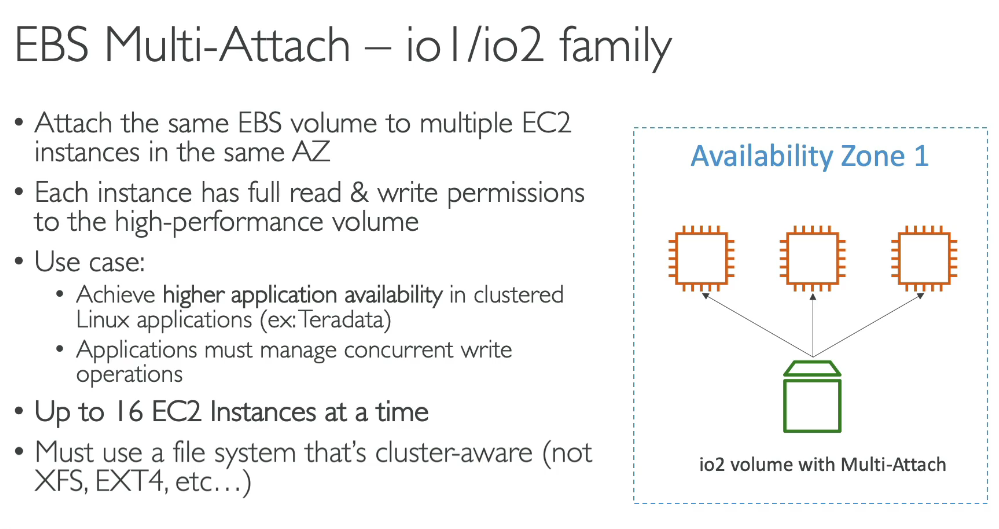
| Provisioned IOPS SSD (io2) | $$$ | 4 GiB – 64 TiB | 256,000 | 4,000 MiB/s | 99.999% | High-performance databases, mission-critical applications requiring low latency |
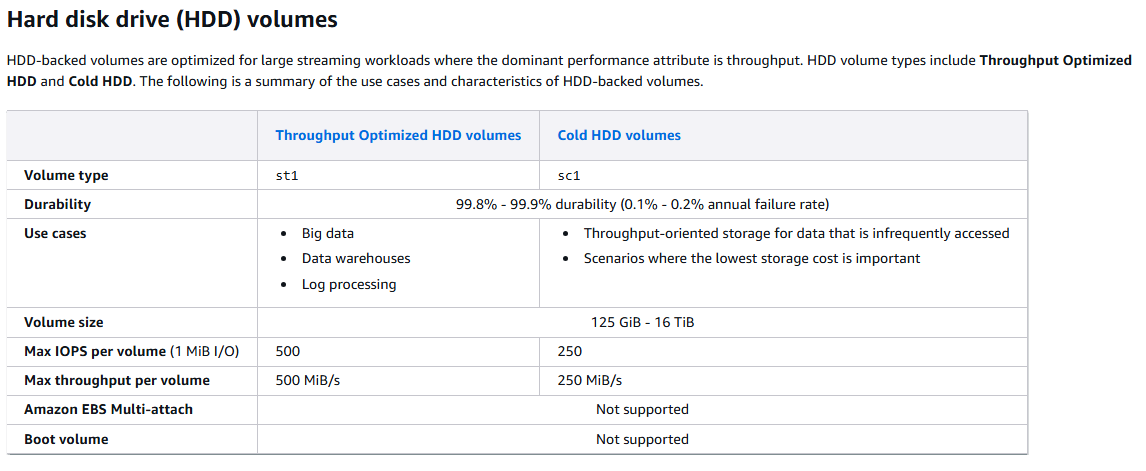
| Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) | $ | 500 GiB – 16 TiB | 500 | 500 MiB/s | 99.8%–99.9% | Big data, data warehouses, log processing, streaming workloads |
| Cold HDD (sc1) | $ (cheapest) | 500 GiB – 16 TiB | 250 | 250 MiB/s | 99.8%–99.9% | Infrequently accessed data, archival storage, backups |
EBS Use Case Recommendations
| Scenario | Recommended EBS Type | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Boot volume for EC2 | gp3 | Balanced performance and cost. |
| High-performance DBs (Oracle, SQL Server) - for database workloads | io2/io1 | Low latency, high IOPS support. |
| Log processing or streaming | st1 | High throughput required for large datasets. |
| Long-term data archiving | sc1 | Cost-effective for rarely accessed data. |
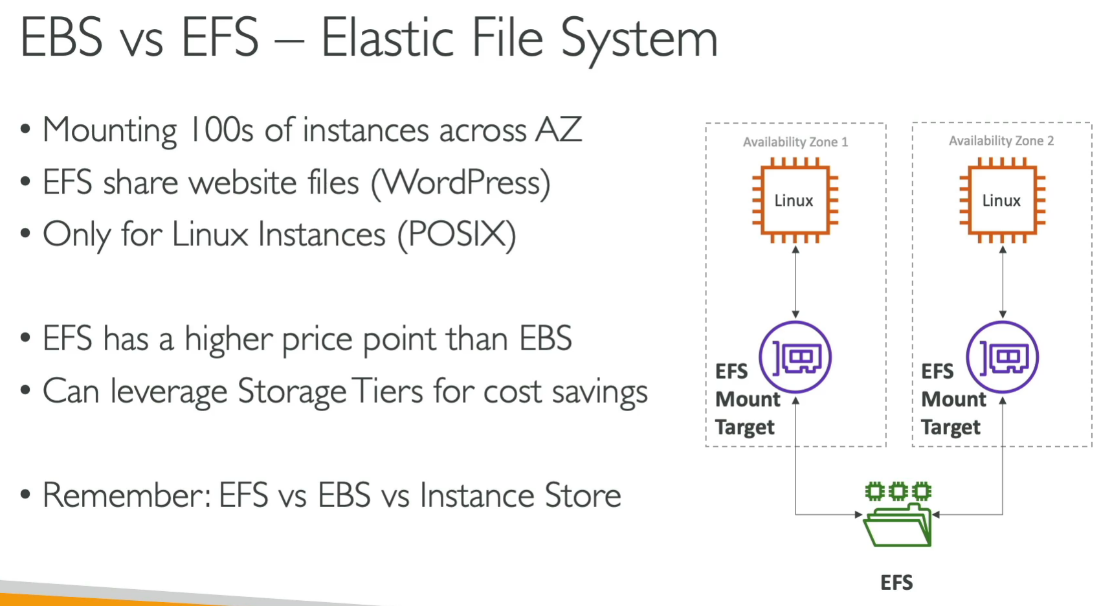
AWS EFS (Elastic File System)